Tornado Safety and Preparedness
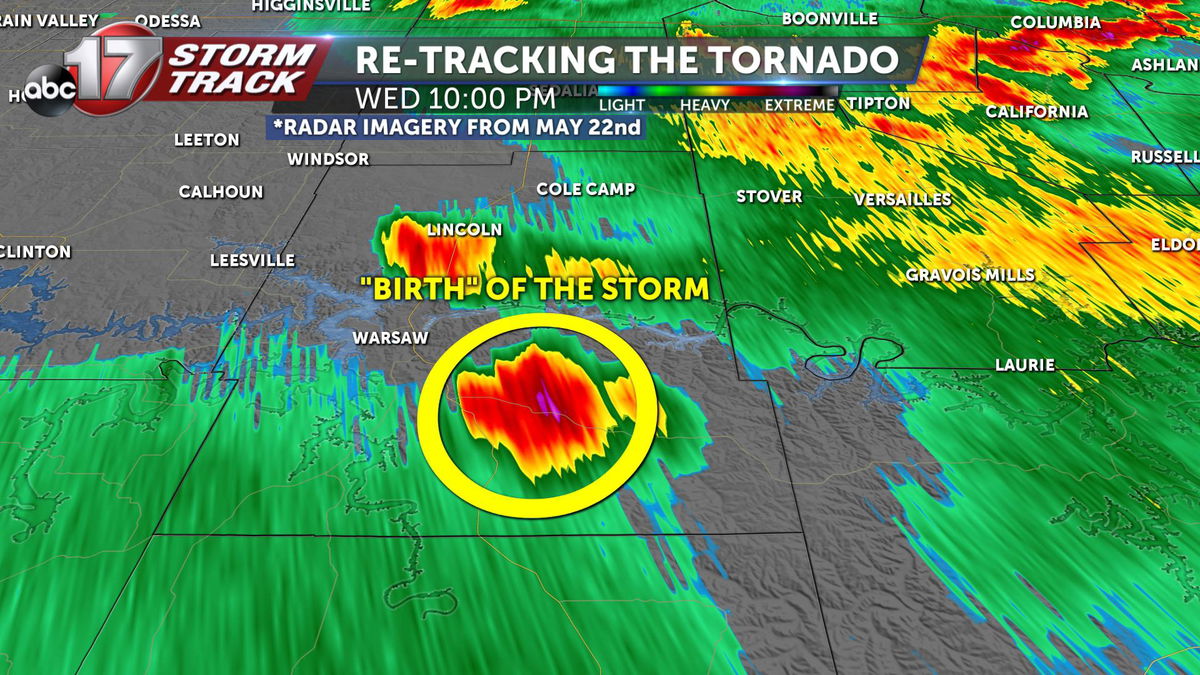
Tornadoes, with their immense power and destructive force, demand our utmost attention and preparation. Understanding the various types of tornado shelters, implementing a comprehensive emergency plan, and recognizing the warning signs of an approaching tornado are crucial for safeguarding lives and property.
Tornado Shelters
Tornado tracker – Tornado shelters serve as a vital lifeline during these hazardous events. Their effectiveness is determined by their construction and design.
- Above-Ground Shelters: These structures are built above the ground level and are typically made of reinforced concrete or steel. They offer a safe haven from the tornado’s powerful winds and debris.
- Underground Shelters: Constructed below ground level, these shelters provide exceptional protection from the tornado’s destructive force. They are often built in basements or specially designed underground rooms.
- Safe Rooms: These are smaller, fortified rooms within a building that are designed to withstand the impact of a tornado. They are typically constructed with reinforced walls and ceilings.
Emergency Preparedness Plan, Tornado tracker
Having an emergency plan in place is essential for tornadoes. This plan should Artikel the steps to be taken before, during, and after a tornado event.
- Before a Tornado: Identify a designated safe shelter, prepare an emergency kit with essential supplies (water, food, first-aid), and stay informed about weather forecasts.
- During a Tornado: Seek immediate shelter in the designated safe place, stay away from windows, and cover your body with blankets or pillows for protection.
- After a Tornado: Check for injuries, report any damage to authorities, and avoid entering damaged buildings until they are deemed safe.
Warning Signs and Actions
Recognizing the warning signs of an approaching tornado is crucial for taking timely action.
- Dark, Rotating Cloud: A funnel-shaped cloud that extends from the base of a thunderstorm is a telltale sign of a tornado.
- Loud Roaring Sound: A tornado often produces a distinct roaring or rumbling sound that can be heard from a distance.
- Debris in the Air: If you observe debris swirling in the air, it may indicate the presence of a nearby tornado.
Upon observing any of these warning signs, take immediate shelter in a designated safe place and stay informed about the latest weather updates.
Tornado Climatology and Forecasting: Tornado Tracker
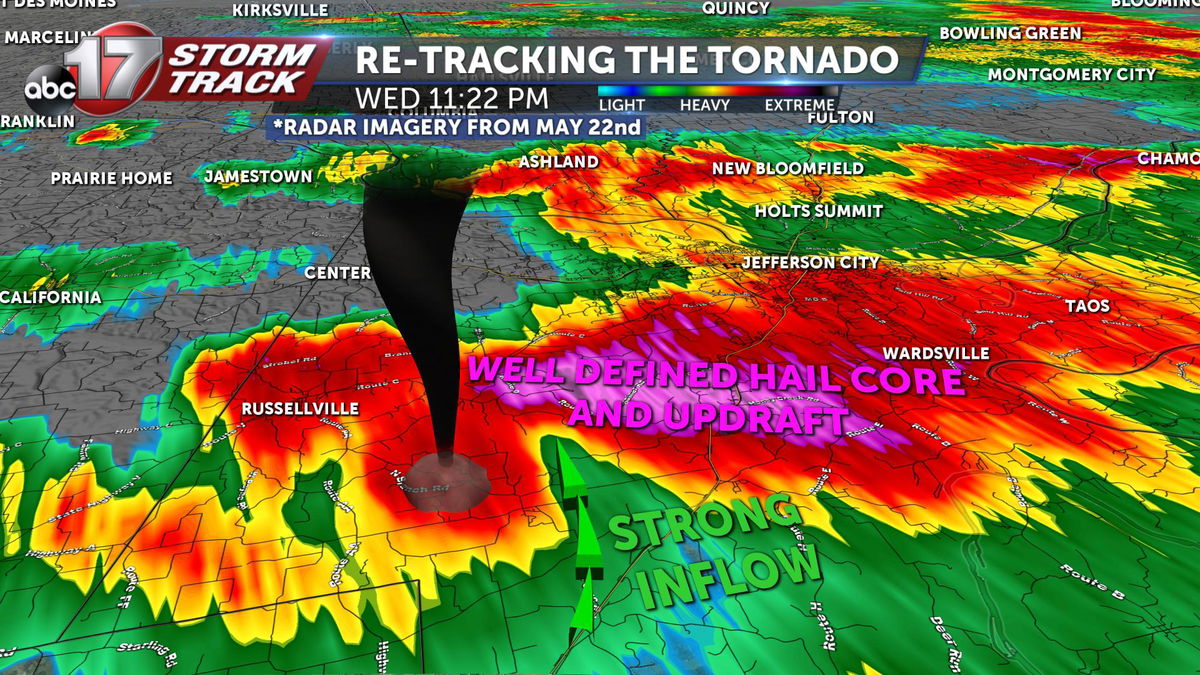
Tornadoes, violent rotating columns of air extending from the base of a thunderstorm cloud to the ground, are fascinating yet destructive weather phenomena. Understanding their climatology and the factors influencing their formation and intensity is crucial for effective forecasting and timely warnings.
Tornadoes exhibit distinct geographical and temporal patterns. They are most common in the central United States, particularly in the “Tornado Alley” region, which stretches from Texas to Nebraska. Other tornado-prone areas include the southeastern United States, the Great Plains, and parts of South America, Europe, and Australia. Tornadoes typically occur during the spring and summer months when atmospheric conditions are favorable for their development.
Factors Influencing Tornado Formation and Intensity
The formation of tornadoes is a complex process influenced by several atmospheric factors. These include:
– Vertical wind shear: Differences in wind speed and direction with height create a rotating motion within the thunderstorm updraft.
– Instability: Warm, moist air near the ground and cooler, drier air aloft provide the energy necessary for thunderstorm development.
– Lifting mechanism: A trigger, such as a cold front or dry line, forces the warm, moist air upward, initiating the thunderstorm updraft.
The intensity of a tornado is determined by the strength of the rotating updraft and the amount of available energy. Stronger updrafts and higher instability contribute to more intense tornadoes.
Role of Weather Forecasting in Predicting and Tracking Tornadoes
Weather forecasting plays a critical role in predicting and tracking tornadoes. Meteorologists use a variety of tools and techniques to monitor atmospheric conditions and identify areas at risk. These include:
– Numerical weather prediction models: Computer models simulate atmospheric conditions and predict future weather patterns.
– Doppler radar: Radar detects the movement and intensity of precipitation, providing valuable information about the structure and rotation of thunderstorms.
– Spotter networks: Trained volunteers and weather enthusiasts report tornado sightings, helping to verify and track tornadoes.
By combining these tools, meteorologists can issue tornado warnings and watches, providing timely information to communities and emergency responders.
Amidst the whirling winds and ominous skies, tornado trackers stand as vigilant guardians, their eyes scanning the horizon for nature’s fury. Their unwavering pursuit of knowledge brings them face to face with phenomena like tropical depression beryl , a swirling vortex that threatens coastal communities.
Yet, these trackers remain undeterred, their determination fueled by the understanding that every moment spent in the field brings them closer to unraveling the mysteries of the storm.
In the heart of the storm, where the tornado’s fury unfurls, the intrepid tornado tracker stands steadfast, their gaze fixed upon the relentless dance of nature. As the tempest rages, their eyes are drawn to Clarksville, a city where the weather whispers secrets of its own.
The Clarksville weather observatory becomes a sanctuary, a haven where the tracker can decipher the symphony of wind and rain, unraveling the patterns that guide the tornado’s path.